SQL uses a virtual account so its not always easy to set the permissions. To do this, go into the security tab and add a new user. Change the Location to the Local Machine, then enter the following name MSSQL$[InstanceName]
- Using Windows Explorer, navigate to the file system location where the database files are stored. Right-click the file system folder, and then clickProperties.
- On the Security tab, click Edit, and then Add.
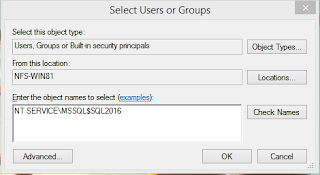
- In the Select Users, Computer, Service Account, or Groups dialog box, click Locations, at the top of the location list, select your computer name, and then click OK.
- In the Enter the object names to select box, type the name of the per-service SID name listed in the Books Online topic Configure Windows Service Accounts and Permissions. (For the Database Engine per service SID name, use NT SERVICE\MSSQLSERVER for a default instance, orNT SERVICE\MSSQL$InstanceName for a named instance.)
- Click Check Names to validate the entry. (If the validation fails, it might advise you that the name was not found. When you click OK, a Multiple Names Found dialog box appears. Now select the per-service SID name, either MSSQLSERVER or NT SERVICE\MSSQL$InstanceName, and then click OK. Click OK again to return to the Permissions dialog box.)
- In the Group or user names box, select the per-service SID name, and then in the Permissions for
box, select the Allow check box forFull control. - Click Apply, and then click OK twice to exit.
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj219062.aspx

No comments:
Post a Comment